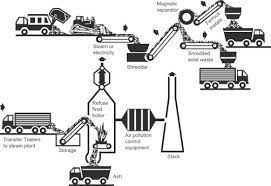
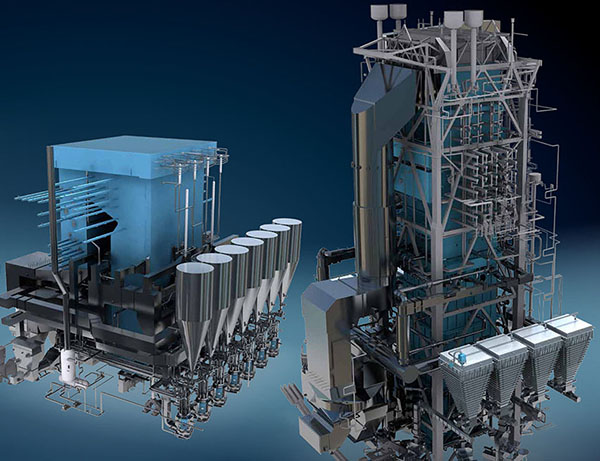
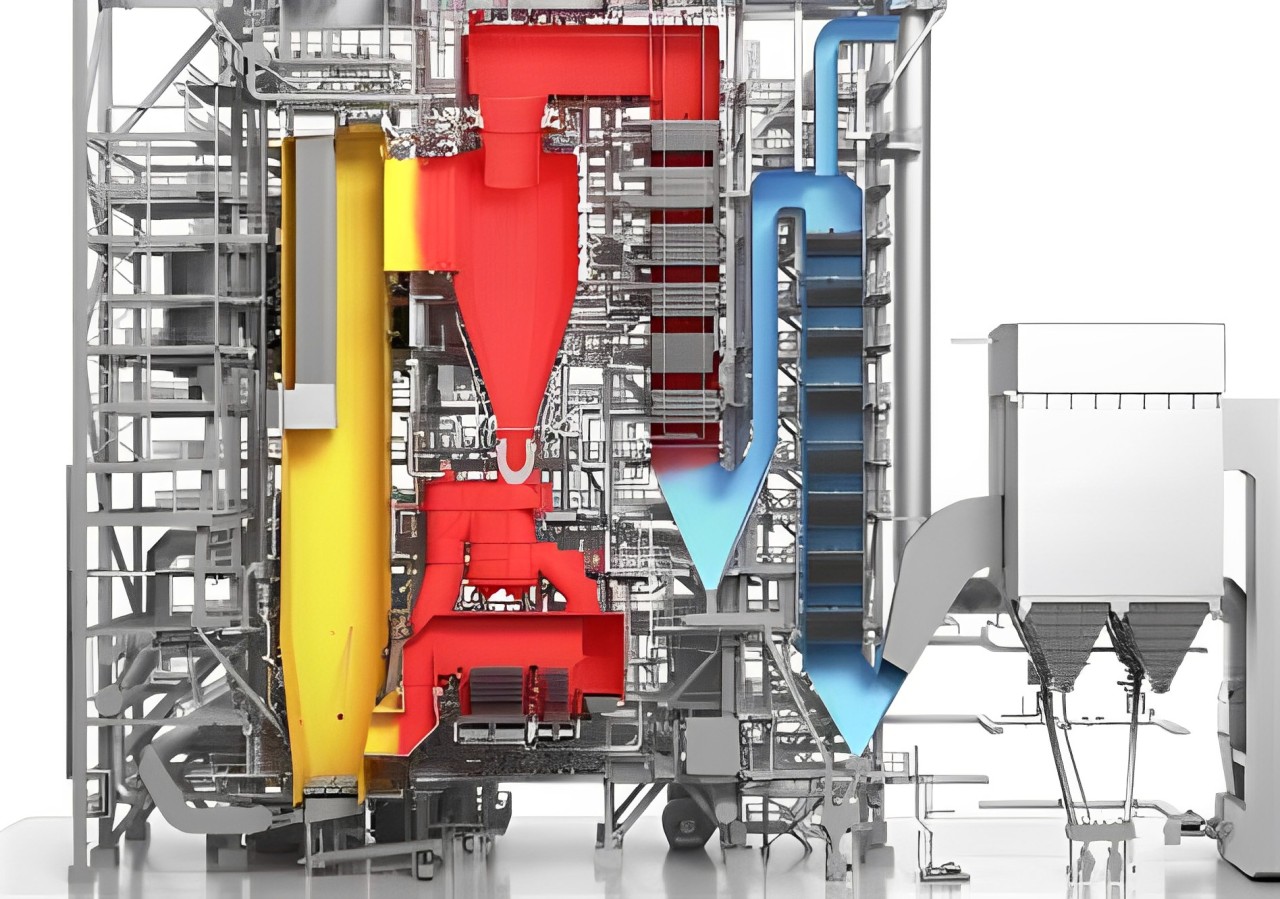
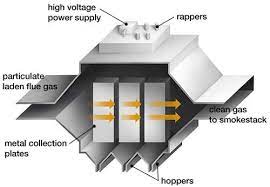
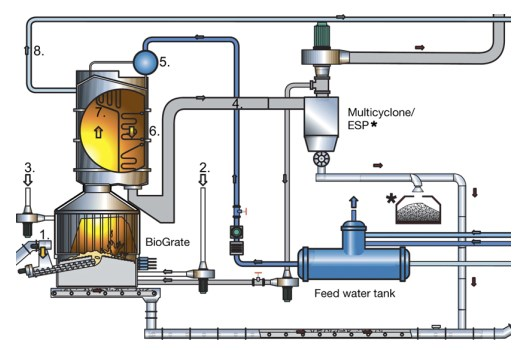
AFBC Bolier:
AFBC (Atmospheric Fluidized Bed Combustion) boilers are a type
of industrial boiler renowned for their versatility and efficiency. In AFBC boilers, solid
fuels are burnt in a fluidized bed of inert particles, ensuring thorough combustion and
reduced emissions. These boilers can handle a wide rang of fuel types, including coal,
biomass, and waste materials, making them suitable for various industries and applications.
One of the key advantages of AFBC boilers is their ability to control combustion
temperatures effectively, leading to lower NOx emissions compared to conventional
boilers. The fluidized bed combustion process also facilitates efficient heat
transfer, resulting in higher thermal efficiency and better fuel utilization.
Additionally, AFBC boilers are known for their flexibility in adapting to
fluctuating fuel qualities and load demands, making them a preferred choice for
many industries seeking reliable and environmentally friendly energy solutions.
AFBC boilers offer operational flexibility, allowing for quick startups and
shutdowns, as well as easy maintenance.
BFBC BOILER:
A BFBC (Bubbling Fluidized Bed Combustion) boiler is another type of
fluidized bed combustion boiler,similar to AFBC boilers but with some differences in operation
and design. In BFBC boilers, the bed of inert material, such as sand or limestone, bubbles
like a boiling liquid due to the upward flow of air or gas through the bed.
BFBC boilers are often used for smaller-scale applications or in situations where
a smaller boiler size is preferred. They can still efficiently burn a variety of fuels,
including coal, biomass,and waste, while offering benefits such as better fuel
flexibility and lower emissions compared to traditional combustion technologies.One
notable advantage of BFBC boilers is their ability to handle fuels with higher moisture
content,which can be advantageous in certain applications. Additionally, BFBC boilers
can be more compact than other types of boilers, making them suitable for installations
where space is limited.
DUMPING GRATE BOILER:
Dumping grate boiler refers to a type of solid fuel-fired boiler equipped with a
dumping grate. A dumping grate is a combustion grate where the fuel is fed onto the grate
and burned as it moves downward. This type of grate allows for the efficient combustion of
various solid fuels, such as coal, biomass, or waste.Dumping grate boilers are commonly
used in industries where solid fuels are abundant and need to be efficiently burned to
generate steam or heat. These boilers are often found in industries such as pulp and paper,
sugar, textile, and wood processing plants. They are known for their robustness and ability
to handle a wide range of solid fuels, including those with varying moisture content and
particle sizes.The operation of a dumping grate boiler involves the controlled feeding of
fuel onto the grate,where it undergoes combustion, and the resulting ash is discharged from
the bottom of the grate.These boilers can be designed for various capacities and operating
conditions to meet the specific requirements of different industrial applications.
RG BOILER :
Reciprocating grate boilers are a type of biomass combustion system
commonly used in industrial
settings for steam generation. In these boilers, biomass fuels such as wood chips, agricultural
residues, or urban waste are fed onto a continuously moving grate. The grate moves back and
forth in
a reciprocating motion, facilitating the controlled combustion of the fuel.
One of the main advantages of reciprocating grate boilers is their ability to handle a wide
range of
biomass fuels with varying moisture content and particle sizes. The reciprocating motion of the
grate helps to ensure thorough mixing of the fuel bed, promoting efficient combustion and
reducing
emissions.
Additionally, reciprocating grate boilers are known for their reliability and durability, making
them suitable for continuous operation in industrial applications. They are often used in
industries
such as pulp and paper, food processing, and power generation, where biomass residues are
readily
available and can be used as a renewable and sustainable fuel source.



.png)